yield point tensile test definition|difference between yield strength and point : warehouse Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) . 30 de abr. de 2021 · Share your videos with friends, family, and the world
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 22 de fev. de 2013 · The new album “Sometime Last Night” featuring “All Night” + more is available now!iTunes: http://smarturl.it/r5a2 Amazon: http://smarturl.it/r5ama2 Google Pl.
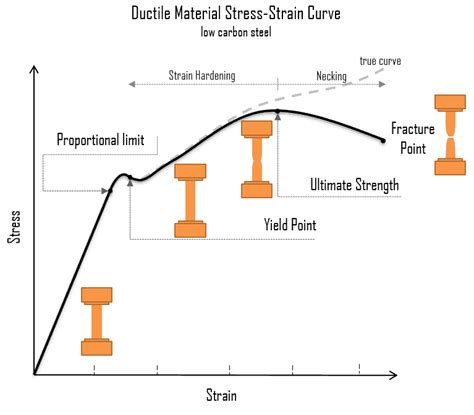
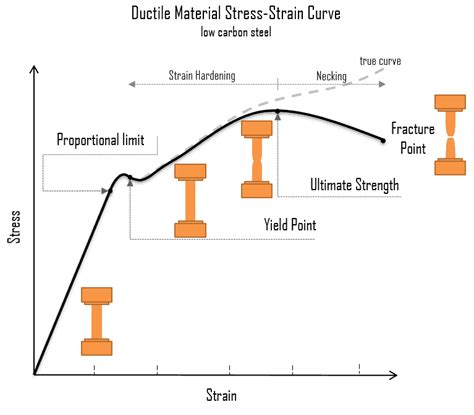
Tensile testing is a destructive test process that provides information about the tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility of the metallic material. It measures the force required to break a composite or plastic specimen and the extent to which the specimen stretches or elongates to .Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) .During monotonic tensile testing, some metals such as annealed steel exhibit a distinct upper yield point or a delay in work hardening. These tensile testing phenomena, wherein the strain increases but stress does not increase as expected, are two types of yield point elongation. Yield Point Elongation (YPE) significantly impacts the usability of steel. In the context of tensile testing and the engineering stress-strain curve, the Yield Point is the initial stress level, below th. The yield point is the point on a material’s stress-strain graph at which it stops deforming elastically and starts deforming plastically. During elastic deformation, the material will return to its original dimensions, but plastic .
This point, known as the yield point, is critical in determining a material’s suitability for various applications. Measurement of Yield Strength. The measurement of yield strength is typically conducted through tensile testing, .The yield point is a critical parameter in studying tensile strength at yield. It refers to the point on the stress-strain curve where a significant increase in strain occurs with minimal or no increase in stress. The upper yield point is defined by the tensile standard ISO 6892-1 for metals as follows: “After reaching the stress maximum, there must be a stress reduction of at least 0.5% . The tensile test is used to determine the strength (yield point, ultimate tensile strength) and toughness (elongation at break) of a material!
Tensile tests are used to determine the modulus of elasticity, elastic limit, elongation, proportional limit, reduction in area, tensile strength, yield point, yield strength and other tensile . Setup. The tensile test is one of the most important testing methods for characterizing or obtaining material parameters. In the tensile test, for example, it is determined which load a material can withstand until it begins .What are the test methods to measure tensile properties of plastics? In general, “tensile test methods” measure the modulus of elasticity of materials. The common methods used are: ASTM D638 - Standard Test Method for Tensile . What is a tensile test?In the field of materials science and engineering, a tensile test is a widely used method to determine the mechanical properties of a material, specifically its response to tensile forces. It involves subjecting a specimen to an ever-increasing tensile load until it reaches its breaking point. By measuring the applied force and the resulting .
The reversal point is the maximum stress on the engineering stress–strain curve, and the engineering stress coordinate of this point is the ultimate tensile strength, given by point 1. Ultimate tensile strength is not used in the design of ductile static members because design practices dictate the use of the yield stress. It is, however .Elongation at Yield is the ratio between increased length and initial length at the yield point. In an ASTM test of tensile strength, the test specimen is pulled from both ends. As the pulling progresses, the specimen bar elongates at a uniform rate. This elongation is proportionate to the rate at which the load or pulling force increases.
Critical in composite testing is alignment due to anisotropy, where material properties vary based on force direction.Aligning tests with the fiber orientation is vital for accurate results, especially in the aerospace industry where composites face high-tensile-stress applications. Various gripping mechanisms are available for ambient, sub-ambient, and high .The strength of a material can be determined by a test known as the tensile test. In this test, the material is mercilessly pulled from both ends. . Yield Point. The yield point is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically. After the yield point is passed, permanent plastic deformation occurs.Yield Point; It is the stage at which the material starts to deform plastically. After the yield point is crossed, permanent deformation occurs. There are two divisions in this: the upper yield point and the lower yield point. Ultimate Stress Point; It is the maximum limit of stress that a material can take before failing. After this point .The yield point is the stress level at which a material begins to deform plastically, marking the transition from elastic behavior to permanent deformation. Beyond this point, any increase in stress will result in significant and irreversible changes to the material's shape or structure, which is crucial for understanding how materials behave under load.
For the evaluation of strength properties, upper and lower yield points, as well as breaking strength or tear strength are determined in addition to the tensile strength.. Yield point is generally defined as the stress at the transition from elastic to plastic deformation. It is the generic term for elastic limit, upper and lower yield strength (tensile test), compressive yield strength .In engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain.It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and strain can be determined (see tensile testing).These curves reveal many of the properties of a material, such as the Young's . Tensile testing, in which a material specimen is subjected to increasing tensile forces until it reaches the point of yielding, is commonly used to assess yield strength. Known as the yield point or yield stress, this is distinguished by a clear departure from the linear elastic area of the stress-strain curve.
Tensile tests are used to determine the modulus of elasticity, elastic limit, elongation, proportional limit, reduction in area, tensile strength, yield point, yield strength and other tensile properties. The main product of a tensile test is a load versus elongation curve which is then converted into a stress versus strain curve. Exploring Elongation TestingElongation testing, a cornerstone of material science, reveals a material's ductility and strength when under tensile stress. By stretching a sample until it breaks, this test measures how much a material can deform before failing. In industries prioritizing safety and durability like automotive and construction, this insight is crucial. .Yield Point. The yield point marks the end of the elastic deformation region and the beginning of the plastic deformation region. It is characterized by a sharp bend in the stress-strain curve at the end of the elastic region. Materials that .
Tensile strength is the resistance of steel to breaking under tensile tension. It’s used to specify the point when steel goes from elastic (temporary) to plastic (permanent) deformation. Usually, it’s measured in units of force per cross . A tensile test is used to determine the yield point or yield strength, tensile strength or ultimate tensile stress, and percentage elongation of a metal. The tensile Testing method measures the force required to break a . The yield point is the boundary between elastic deformation and plastic deformation. Before the yield point, a material bends by stretching atomic bonds. Beyond the yield point, the atoms have stretched to their limit and further deformation happens because atoms move past each other. On a stress-strain curve, the yield point is the point where the .That’s why we’ve put together a quick and handy guide to yield strength testing. Understanding yield strength. The yield point, or yield strength, is the point on a stress–strain curve where elastic behavior ends, and plastic behavior begins. Put simply, yielding describes the start of breaking of fibers on the sample being tested.
test de que vision tienes en genshin impact
The ASTM E8 / ASTM E8M standard describes uniaxial tensile testing of metals at room temperature and the determination of characteristic values including yield strength, yield point, yield point elongation, tensile strength, strain at break and reduction of area. The values can be used to make predictions about the strength and toughness of the . Yield Stress | Definition & Formula . The graph of a material's stress versus strain data from a tensile or compression test is called a stress-strain curve. Figure 5 is an example of a tensile . Tensile testing is arguably the most common test method used in both force measurement and material testing. Tensile testing is used primarily to determine the mechanical behavior of a component, part or material under static, axial loading. The test method for both material testing and force measurement is similar; however the measurement results are .
Also known as yield strength, the yield point definition is the maximum stress that can be applied to a material without it suffering permanent or irreversible deformation. Thus, if a stress . Key Point: Irreversible and indicates that the material’s elastic limit has been exceeded. Brittle Deformation: Definition: Sudden and catastrophic failure of a material without any prior plastic deformation. Key Point: Characterized by low ductility and a high susceptibility to fracture. Tensile Strength: The Breaking Point of Materials
The yield point of a material is a mechanical property commonly measured during materials testing. The yield point of a material occurs when the material transitions from elastic behavior - where removing the applied load will return the material to its original shape - to plastic behavior, where deformation is permanent.A tensile test is a primary mechanical property testing method in which a specimen is pulled out by unidirectional tensile forces until fracture failure. The mechanical characteristics which are directly found out from tensile test are ultimate tensile strength, maximum elongation, yield strength, maximum force, and area reduction.The definition of the tensile stress is \[tensile\; stress = \frac{F_{\perp}}{A} \ldotp \label{12.34}\] Tensile strain is the measure of the deformation of an object under tensile stress and is defined as the fractional change of the object’s length when the object experiences tensile stress
yield point definition engineering
what is yield point strength
tensile testing process
webShinobi Warfare cheats. Free mods and trainers for Shinobi Warfare, and thousands of your favorite single-player PC games — all in one place. . Get Started .or visit us on your PC to download the app 5/5 Trustpilot rating. See how it works. Download Download for Windows 85 MB. Get Started .or visit us on your PC to download the app 5/5 .
yield point tensile test definition|difference between yield strength and point